Project Background and Personal Journey
This project was motivated by the growing challenges in managing water resources efficiently, especially water loss caused by undetected leaks, poor monitoring, and delayed response. Existing systems often depend on manual checks and lack real-time visibility, which leads to excessive wastage and slow maintenance. Seeing how these issues affect both communities and authorities inspired me to work on a smarter, technology-driven solution.
During this project, I explored how sensor data, automation, and mobile applications can work together to improve water management. I focused on designing an application that clearly presents critical information such as water flow status, leak alerts, GPS-based locations, and water quality readings. One of my key learnings was how to simplify complex technical data into an interface that is easy to understand and act upon.
This journey helped me move beyond just building a system to thinking about usability, clarity, and real-world impact. It strengthened my ability to translate engineering concepts into meaningful user experiences and deepened my interest in designing solutions that solve practical problems while contributing to sustainability and public welfare.
Problem
Water distribution systems suffer from significant water loss due to undetected leaks, delayed response, and inefficient monitoring. Most existing systems rely on manual intervention and lack real-time visibility of water flow, quality, and fault location. Poor communication between users and authorities further delays repairs, leading to water wastage, service interruptions, and increased maintenance challenges.
Research
Smart Water Management App is designed based on an Arduino-powered system that monitors real-time water flow, detects pipeline leaks, tracks water quality using a TDS sensor, and identifies leak locations through GPS. The app notifies municipal officers instantly, allows remote motor control to stop water flow during leaks, and enables users to register and track complaints, helping reduce water loss and improve efficient water distribution.
User Survey
The user survey focused on understanding challenges faced by residents and authorities in managing water supply systems. Most users reported frequent water leakage issues, delayed repairs, and difficulty in informing authorities about problems. They also expressed concern over water quality and the lack of transparency in knowing supply status.
Authorities highlighted challenges in locating leaks accurately and responding quickly due to missing real-time data. Both groups emphasized the need for a simple mobile application that provides real-time alerts, leak location details, water quality information, and a clear complaint-tracking system to reduce water loss and improve response efficiency.
Block Diagram & Working Process
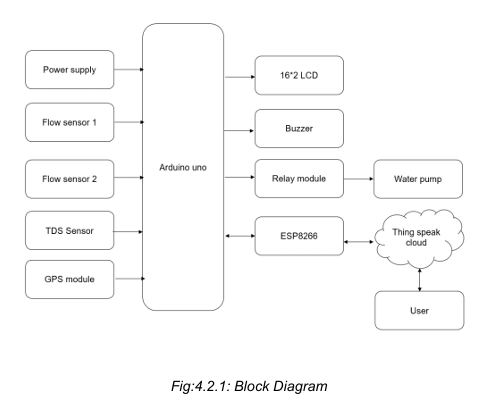
The provided Fig:4.2.1 illustrates the Smart Water Management System, which integrates various components to efficiently monitor and control water flow and quality. At the core of the system is the Arduino Uno, which acts as the central controller, processing data from multiple sensors and managing connected devices. The system receives power from a dedicated power supply to ensure stable operation. Two flow sensors monitor water flow rates in different pipelines, while the TDS sensor evaluates water quality by measuring dissolved solids. The GPS module plays a crucial role in locating detected issues, such as leaks or contamination, providing precise coordinates for efficient maintenance. The Arduino Uno displays real-time data on a 16x2 LCD screen and triggers a buzzer alert during faults or abnormal conditions. The relay module, controlled by the Arduino, regulates the water pump to stop water flow when a problem is identified.
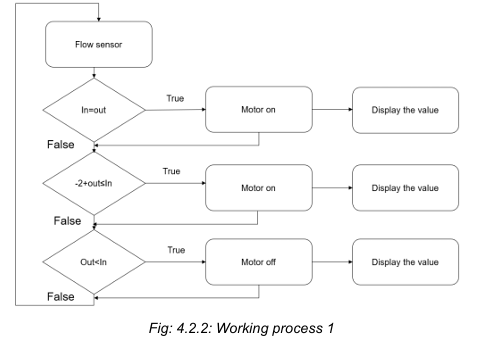
The process starts with the flow sensor measuring water flow values at the inlet (In) and outlet (Out). The first decision checks if the inlet and outlet values are equal. If true, the motor turns on, and the value is displayed. If false, the next condition verifies if the inlet value is within a tolerance range of -2+out≤In. If true, the motor remains on, and the value is displayed. If this condition also fails, the system checks if the outlet value is less than the inlet value. If true, the motor is turned off, and the value is displayed. If none of these conditions are met, the system loops back for continuous monitoring. This structured logic ensures the motor operates efficiently, maintaining water flow control and preventing potential leaks or overflow.
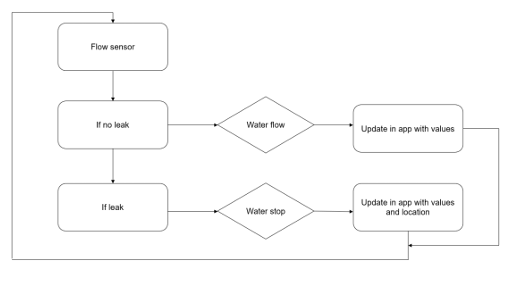
The process begins with the flow sensor measuring water flow values. If no leak is detected, the system verifies the water flow status, updates the app with the corresponding values, and continues monitoring. If a leak is detected, the system identifies a water stop condition, updates the app with both the values and the leak's location, and loops back for continuous observation. This system effectively combines real-time monitoring, data updating, and alert mechanisms to ensure efficient water management.
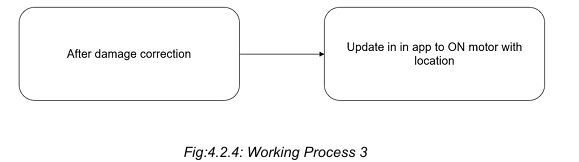
Once the damage is repaired, the system updates the app with the relevant information, including the motor's ON status, the location of the correction, and the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) values. This ensures that the system resumes normal operation while providing essential data for monitoring water quality and system functionality.
Data Collection
The system collects real-time data from multiple sensors integrated with the Arduino controller. Flow sensors continuously measure inlet and outlet water flow to detect leaks, while the TDS sensor monitors water quality levels.
A GPS module captures the exact location of detected issues. This sensor data is transmitted via a Wi-Fi module to the cloud and mobile application, where it is stored and displayed for users and municipal authorities.
The collected data supports real-time monitoring, alert generation, complaint tracking, and analysis of water usage patterns for better decision-making.
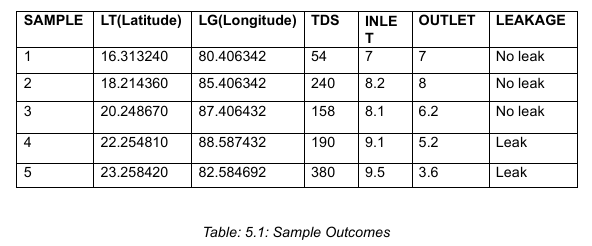
Data Analysis & Results
The collected sensor data shows clear differences between normal water flow and leakage conditions. When inlet and outlet flow values are almost equal, the system identifies normal operation and no leakage is detected. In cases where a significant drop is observed between inlet and outlet flow values, the system successfully detects a leak and automatically stops the motor to prevent water wastage.
TDS values vary across locations, highlighting changes in water quality and reinforcing the importance of continuous monitoring. GPS coordinates captured during leakage events help accurately locate the affected area, enabling faster response by authorities. These results confirm that the system effectively combines flow analysis, water quality monitoring, and location tracking to support real-time decision-making and efficient water management.
Design Decisions
Real-time alerts: Real-time alerts were prioritized to ensure immediate notification during water leakage or abnormal flow conditions, helping authorities take quick action and reduce water wastage.
Highlighted key metrics on the dashboard: Critical data such as inlet–outlet flow values, leak status, TDS levels, and motor status were highlighted to give users and authorities a quick understanding of the system without cognitive overload.
Simple motor control & status indicators: Motor ON/OFF controls and status indicators were kept simple to avoid confusion during emergency situations and enable fast, error-free decision-making.
Solution Overview
The solution is a Smart Water Management system that combines an Arduino-based hardware setup with a user-friendly mobile application. Flow sensors continuously monitor inlet and outlet water flow to detect leaks, while a TDS sensor tracks water quality in real time. When abnormal conditions are detected, the system automatically stops the water motor and sends instant alerts to the app.
GPS integration provides the exact location of the issue, enabling faster maintenance. The app also allows users to raise complaints and authorities to remotely control the motor, creating an efficient, centralized solution to reduce water wastage and improve response time.
Usability Testing
Usability testing was conducted using an interactive prototype of the Smart Water Management App. Users were asked to perform key tasks such as checking leak status, viewing water quality data, locating issues on the map, and controlling the motor. The testing showed that users could easily understand the dashboard and complete tasks with minimal guidance.
Feedback helped refine icon clarity, improve status labels, and simplify navigation. These iterations ensured the app remains intuitive, efficient, and easy to use for both users and authorities.
Results & Impact
The Smart Water Management system successfully detected water leaks in real time and reduced unnecessary water loss by automatically stopping the motor during abnormal conditions.
GPS-based location tracking enabled faster identification of leakage points, improving maintenance response time. Continuous water quality monitoring increased transparency and safety for users.
The mobile app improved communication between users and authorities by providing clear alerts, live data, and complaint tracking. Overall, the solution demonstrated improved efficiency, quicker decision-making, and a more reliable approach to sustainable water management.
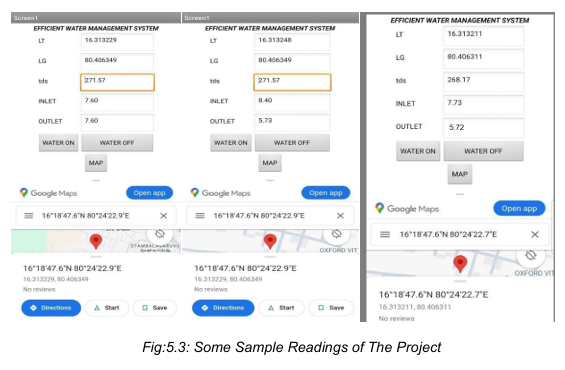

User Interface Design
The user interface was designed with a focus on clarity, simplicity, and quick decision-making. A clean dashboard presents critical information such as inlet–outlet flow values, leak status, TDS levels, motor state, and GPS location without clutter. Visual indicators and clear labels help users instantly understand system status, especially during emergency situations.
Navigation was kept minimal to reduce cognitive load, while action buttons like motor control and map view were made easily accessible. The overall design ensures both users and authorities can monitor, respond, and manage water issues efficiently.
This Project Taught Me
This project taught me how to transform complex technical data into a clear and usable digital experience. I learned the importance of designing for real-world constraints such as time-critical alerts, system reliability, and user clarity during emergencies.
Working on this project strengthened my ability to think from both a system and user perspective, balance functionality with simplicity, and design interfaces that support quick decision-making. Most importantly, it helped me understand how thoughtful design can create practical impact and contribute to sustainable solutions.